 Launch apps instantly. Claim $200 credits on DigitalOcean
Launch apps instantly. Claim $200 credits on DigitalOcean
Written by rahulpatel07 » Updated on: March 01st, 2024
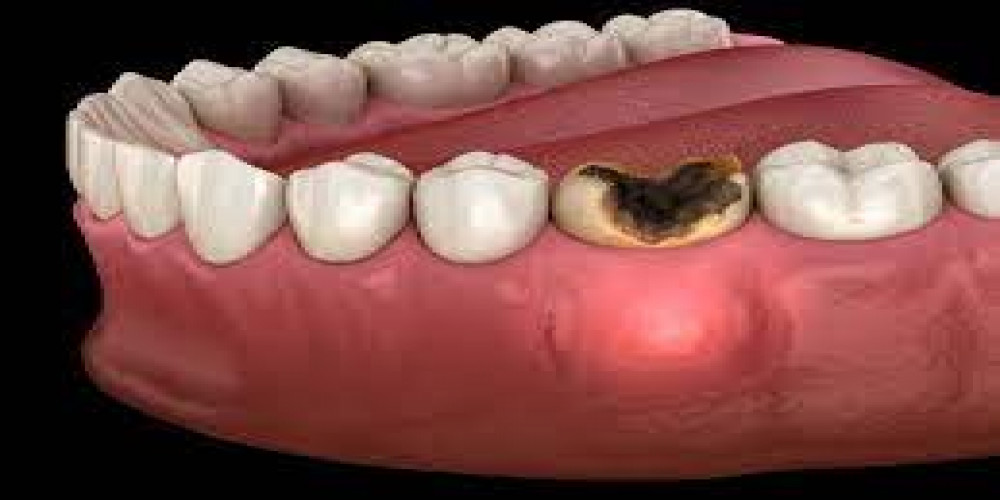
Tooth infections, although appearing minor, may pose serious risks if left untreated. While the course and severity of a tooth infection might differ, recognising the possible timetable and dangers connected with its spread is critical for prompt treatment. In this detailed post, we will look at the phases of a tooth infection, the possible repercussions, and how to successfully reduce the dangers.
Stages of Tooth Infection:
Initial Stage:
A tooth infection usually starts with the invasion of germs into the tooth’s pulp, which is generally caused by untreated dental decay or trauma.
Initially, the infection may cause minor pain or sensitivity to hot and cold foods and drinks.
Without action, the infection develops, destroying tooth structure and forming an abscess.
Intermediate Stage:
As the infection progresses, symptoms worsen, including chronic toothache, swelling of the gums or face, and the appearance of a pimple-like protrusion on the gums (abscess).
Without quick treatment, the infection may spread to other tissues, including the jawbone and neighbouring teeth.
Advanced Stage:
In the absence of proper dental care, a tooth infection may cause systemic issues such as the spread of germs into the bloodstream (bacteremia).
Bacteremia caused by a dental infection may possibly harm essential organs such as the heart, lungs, or brain, leading to life-threatening diseases if left untreated.
Risks and Complications:
Spread of Infection:
One of the most serious hazards of an untreated tooth infection is the spread of germs to surrounding tissues and organs.
This spread may cause dangerous consequences such as Ludwig’s angina (a severe infection of the mouth floor), osteomyelitis (bone infection), and sepsis (blood poisoning).
Impact on overall health:
Chronic tooth infections may have a wide-ranging impact on overall health, leading to illnesses such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.
The immunological response to a prolonged infection may also cause inflammation throughout the body, worsening pre-existing conditions.
Dental complications:
In addition to systemic dangers, untreated tooth infections may cause tooth loss, impaired oral function, and the need for more invasive dental operations, such as root canal therapy or tooth extraction.
Prevention and treatment:
Maintain good oral hygiene.
Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are vital for avoiding dental decay and gum disease, which may lead to tooth infections.
Prompt Dental Care:
Addressing dental disorders, such as cavities or damaged teeth, as soon as possible will help prevent them from escalating to more severe illnesses.
Seeking immediate care for a toothache or dental pain is critical for avoiding the development of infection.
Antibiotics with Dental procedures:
In situations when a tooth infection has already occurred, antibiotics may be recommended to assist stop the spread of germs.
Depending on the severity of the illness, dental operations such root canal therapy or tooth extraction may be required to remove the source of infection.
Healthy lifestyle choices:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet and avoiding tobacco use, may improve general oral and systemic health, lowering the risk of dental infections and problems.
Maintain good oral hygiene.
Good dental hygiene is essential in avoiding tooth infections. This involves using fluoride toothpaste at least twice a day, flossing daily to remove plaque and food debris from between teeth and along the gum line, and using an antiseptic mouthwash to minimise germs in the mouth. Regular dental check-ups and expert cleanings are also vital for recognising and treating tooth problems before they become infections.
Healthy Diet:
A well-balanced diet is important for maintaining dental health. Consuming foods high in vitamins and minerals, especially calcium and vitamin D, helps to build teeth and bones, lowering the risk of tooth decay and infection. Limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks may help to avoid enamel erosion and cavities, both of which can cause to infections.
Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol consumption.
Tobacco use, whether smoking or chewing, increases the risk of gum disease and tooth decay, rendering people more vulnerable to dental infections. Similarly, excessive alcohol intake may impair the immune system and lead to oral health issues. Avoiding smoke and limiting alcohol use might help you maintain good dental health and avoid infections.
Address Dental Issues Promptly:
Cavities, damaged teeth, and gum disease all allow germs to enter the mouth, increasing the chance of having a tooth infection. It is critical to treat these conditions immediately by getting expert dental care. Dentists may use fillings, crowns, or periodontal therapy to repair and preserve the teeth and gums, preventing infections from forming or progressing.
Regular Dental Checkups:
Routine dental checkups are vital for maintaining oral health and detecting illness early. Dentists can discover cavities, gum disease, and other oral problems during check-ups and offer suitable treatments to avoid infections. Furthermore, frequent cleanings eliminate plaque and tartar accumulation, which reduces the likelihood of bacterial development and illness.
Antibiotics with Dental procedures:
If a tooth infection develops, immediate treatment is required to prevent spread and reduce symptoms. Dentists may prescribe antibiotics to kill infection-causing germs and minimise inflammation. In severe cases of infection, it could be necessary to perform dental procedures like root canal treatment or tooth extraction in order to eradicate the illness’s cause and stop it from spreading to other tissues.
Pain Management:
Tooth infections may cause severe pain and suffering. While you wait for dental treatment, over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may help relieve discomfort and inflammation. However, these drugs only give temporary comfort and should not be used as a replacement for expert dental treatment.
Follow-up Care:
After having treatment for a tooth infection, it is critical to follow any post-operative recommendations prescribed by your dentist.
Read More: How to Reduce Gap Between Teeth Naturally at Home?
Visit: Healcard.com
Copyright © 2024 IndiBlogHub.com Hosted on Digital Ocean
Post a Comment
To leave a comment, please Login or Register