 Launch apps instantly. Claim $200 credits on DigitalOcean for free!
Launch apps instantly. Claim $200 credits on DigitalOcean for free!
Written by Desi Gardening » Updated on: April 24th, 2024

Greetings, Desi Gardeners! Composting of waste, an essential facet of horticulture, stands as a paramount component in the world of potting, second only to the soil itself. Indeed, compost serves as a nourishing sustenance and a haven for plants.

Composting, often associated with various manures, encompasses a broader spectrum. Diverse compost types exist, tailored to specific plants. For instance, azaleas predominantly flourish in leaf compost, while mushroom cultivation demands a sterile composting medium.
The crux of composting entails the preparation of plant sustenance through decomposition. While we accumulate kitchen remnants like vegetable peels and tea leaves to nourish our plants, direct application poses challenges. A multitude of insects are drawn to decompose the waste, potentially jeopardizing plant health. Furthermore, decomposition emits heat and eventually releases acidic compounds detrimental to the roots.
In nature's embrace, the Earth harmonizes the heat, insects, and soil pH, metamorphosing waste into compost, and enriching the soil. However, human intervention demands meticulous attention to temperature, moisture, oxygen, and organic constituents to craft compost suitable for plants.
Compost can be categorized into 'green' and 'brown'. 'Green' compost, abundant in nitrogen-based nutrients, contrasts with 'brown' compost, rich in carbon and organic substances.

Aerobic composting stands as a prevalent method. Gardeners often amass dried leaves, twigs, and wood chips in a bin, allowing them to decompose in the open air. Alternatively, utilizing a compost tumbler with added moisture accelerates bacterial decomposition. This method yields compost in approximately two months, emits minimal odor, and offers an eco-friendly approach to reutilizing organic waste, thereby reducing expenses.
Anaerobic Composting of Waste:
In-ground composting, a traditional approach, involves digging a pit and burying kitchen waste, grass clippings, and other organic residues. This method harnesses anaerobic bacteria for decomposition, producing high-quality compost. However, it can be time-consuming and emits odors and methane gas, which is less favorable.Despite these drawbacks, in-ground composting remains a preferred method among farmers.
Vermicompost, often referred to as 'black gold', garners immense admiration among gardeners. This method employs earthworms to decompose organic matter, enhancing soil porosity, and fertility, and facilitating robust plant growth.
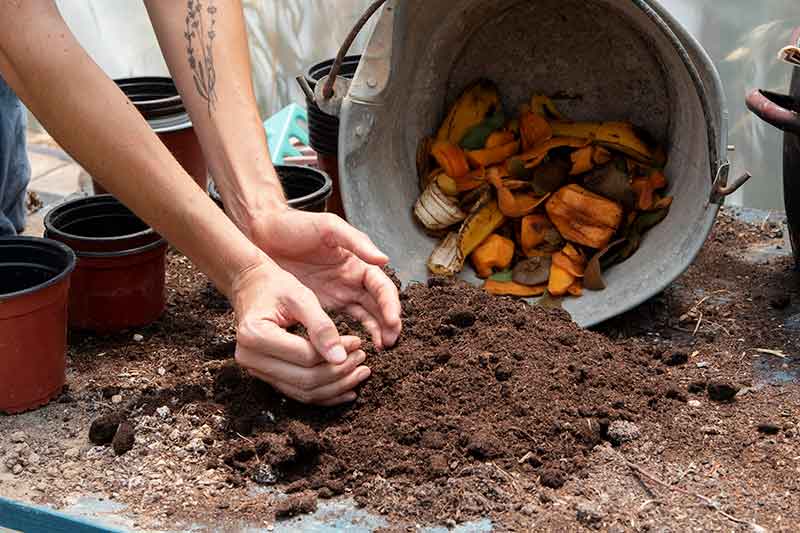
Qualities of Superior Compost
Compost should encompass a diverse range of organic matter. Unless tailored for a specific plant, a balanced N, P, and K composition is indispensable. Both macronutrients and micronutrients are essential at various stages of a plant's life cycle. Excess citrus peels, for example, can acidify the compost, beneficial for plants like hibiscus or roses but unsuitable for lavender.
Inadequately decomposed compost emits an unpleasant odor, attracts pests, and can harm plants. Premium quality compost is devoid of any foul smell.
Ideally, compost should maintain a pH range between 6 and 8, effectively neutralizing soil acidity. Contrary to popular belief, adding compost does not necessarily acidify the soil. Scientific verification through a pH meter is imperative for accurate assessment.
Cow Dung Compost: Before application, cow dung and cow dung cakes should undergo a composting process. Aged cow dung compost, when dried and processed, serves as an exceptional, cost-effective fertilizer. Liquid fertilizer can also be derived by soaking cow dung compost in water.

Mustard Cake Fertilizer and Compost: Extracted from the remaining fiber after oil extraction, mustard cake is dried, composted, and then ready for application. It can be used as a dry or liquid fertilizer.
Market-Sold Compost: An organic blend of various crops, vegetables, fruits, wooden twigs, chips, and animal waste, it serves as a vital potting soil component. Compost tea can also be prepared for plant fertilization.
Vermicompost: Especially crafted with earthworm assistance, vermicompost is highly favored by gardeners. Vermicompost tea serves as a valuable liquid fertilizer.
Leaf Compost: Predominantly made from dried leaves, it is essential for specific plants like azaleas, camellias, rhododendrons, succulents, and cacti.
In essence, the objective of composting is to shield plants from the heat, acids, and odors produced during decomposition. The application of well-prepared compost facilitates easy absorption of nutrients by plants, promoting their growth and blooming.
Copyright © 2024 IndiBlogHub.com Hosted on Digital Ocean